Consider an environment consisting of uncorrelated noise of power σn^2. It is assumed that there is no directional source present. The array signal vector for this case becomes
(2.17) |
The array output is obtained by taking the inner product of weight vector and the array signal vector. Thus,
(2.18) |
Substituting from (2.17) and (2.1), the output becomes
(2.19) |
The mean output noise power of a processor is given by (18). Thus, the mean output power of the conventional processor in the presence of uncorrelated noise only is given by
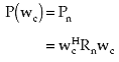 |
(2.20) |
Since Rn is given by
(2.21) |
substituting for Rn and wc in (2.20),
(2.22) |
Thus, the mean power at the output of the conventional processor is equal to the mean uncorrelated noise power at an element of the array divided by the number of elements in the array. In other words, the noise power at the array output is L times less than that present on each element.
Back to conventional beamformer.
Conventional beamformer when a source is in the look direction is discussed here.
Conventional beamformer in the presence of directional interference is discussed here .
Signal to noise ratio (SNR) of a conventional beamformer is discussed here.
Back To Contents .