The conventional beamformer, sometimes also known as the delay-and-sum beamformer, has weights of equal magnitudes. The phases are selected to steer the array in a particular direction (φ0,θ0), known as look direction. With S0 denoting the steering vector in the look direction, the array weights are given by
(2.1) |
The response of a processor in a direction (φ,θ) is obtained by using (1.17), that is, taking the dot product of the weight vector with the steering vector S(φ,θ). With the weights given by (2.1), the response y(φ,θ) is given by
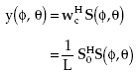 |
(2.2) |
For more information about delay and sum beamformer you can click here.
Conventional beamformer when a source is in the look direction is discussed here.
Conventional beamformer in the presence of directional interference is discussed here.
Conventional beamformer in the presence of an environment consisting of uncorrelated noise is discussed here.
Signal to noise ratio (SNR) of a conventional beamformer is discussed here.
Back To Contents.