Assume that the noise environment consists of the random noise of power σn^2 and a directional interference of power PI in the nonlook direction. Assume that there is a sourceof power PS in the look direction. Given that the interference and the signal are uncorrelated, the array signal vector for this case becomes
(2.23) |
Now we have two directional sources, a signal source, a directional interference, and the random noise. Thus, it follows from (1.22) that the array correlation matrix R is given by
(2.24) |
The mean output power of the processor is given by
(2.25) |
Substituting from (2.1), (2.24) and noting that (S0)H*S0 = L, the expression for the mean output power from (2.25) becomes
(2.26) |
Note that the mean output power of the processor is the sum of the mean output powers due to signal source, directional interference, and uncorrelated noise.
The mean signal power at the output of the processor is equal to the mean power of the signal source, that is,
(2.27) |
The mean noise power is the sum of the interference power and the uncorrelated noise power, that is,
(2.28) |
The output signal to noise ratio is then given by
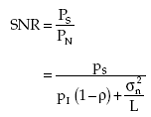 |
(2.29) |
Now consider a special case when no directional interference is present. For this case, the expression for the output SNR becomes
(2.30) |
As the input SNR is PS/σn^2, this provides an array gain, which is defined as the ratio of the output SNR to the input SNR, equal to L, the number of elements in the array.
This processor provides maximum output SNR when no directional interference operating at the same frequency is present. It is not effective in the presence of directional interference, whether intentional or unintentional. The response of the processor toward a directional source is given by (2.2). The performance of the processor in the presence of one nonlook directional source indicated by SNR is given by (2.29). It is a function of the interference power and the parameter ρ that in turn depends on the relative direction of two sources and array geometry.
Back to conventional beamformer.
Conventional beamformer when a source is in the look direction is discussed here.
Conventional beamformer in the presence of directional interference is discussed here.
Conventional beamformer in the presence of an environment consisting of uncorrelated noise is discussed here.
Back To Contents .