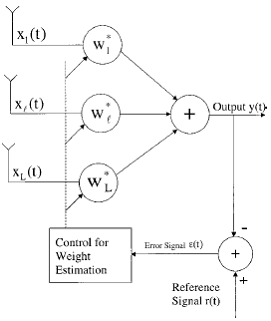
A narrowband beamforming structure that employs a reference signal to estimate the weights of the beamformer is shown in Figure 8.

Figure 8 : An array system using reference signal.
The array output is subtracted from an available reference signal r(t) to generate an error signal ε(t) = r(t) – (w)H*x(t) that is used to control the weights. Weights are adjusted such that the mean squared error between the array output and the reference signal is minimized. The mean squared error ξ(w) for a given w is given by
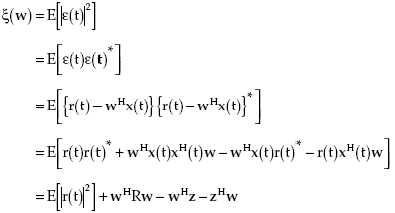 |
(5.1) |
| Where | |
(5.2) |
(5.3) |
|
| Since | |
(5.4) |
|
| Thus | |
(5.5) |
The processor with these weights is also known as the Wiener filter. The minimum MSE ξ of the processor using these weights is obtained by substituting W MSE for w in (5.1), resulting in
(5.6) |
The required reference signal for the Wiener filter may be generated in a number of ways depending on the application. In digital mobile communications, a synchronization signal may be used for initial weight estimation followed by the use of a detected signal as a reference signal. In systems using the TDMA scheme, a user-specific sequence may be part of every frame for this purpose. The use of known symbols in every frame has also been suggested in. In other situations, use of an antenna for this purpose has been examined to show the suitability to provide a reference signal.
In the next page beam space processing is discussed.
Back To Contents .