Steering vector is an L-dimensional complex vector containing responses of all L elements of the array to a narrowband source of unit power. Let Sk denote the steering vector associated with the kth source. For an array of identical elements, it is defined as
| (1.12) |
Note that when the first element of the array is at the origin of the coordinate system τ1(Φk,θk) = 0, the first element of the steering vector is identical to unity.
As the response of the array varies according to direction, a steering vector is associated with each directional source. Uniqueness of this association depends on array geometry. For a linear array of equally spaced elements with element spacing greater than half wavelength, the steering vector for every direction is unique.
For an array of identical elements, each component of this vector has unit magnitude. The phase of its ith component is equal to the phase difference between signals induced on the ith element and the reference element due to the source associated with the steering vector. As each component of this vector denotes the phase delay caused by the spatial position of the corresponding element of the array, this vector is also known as the space vector. It is also referred to as the array response vector as it measures the response of the array due to the source under consideration. In multipath situations such as in mobile communications, it also denotes the response of the array to all signals arising from the source .In the next sections, steering vector, space vector, and array response vector are used interchangeably.
Using (1.12) in (1.10), the signal vector can be compactly expressed as
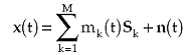 |
(1.13) |
Substituting for x(t) from (1.13) in (4), it follows that
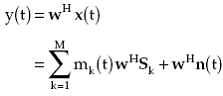 |
(1.14) |
The first term on the right side of (1.14) is the contribution from all directional sources and the second term is the random noise contribution to the array output. Note that the contribution of all directional sources contained in the first term is the weighted sum of modulating functions of all sources. The weight applied to each source is the inner product of the processor weight vector and steering vector associated with that source, and denotes the complex response of the processor toward the source. Thus, the response of a processor with weight vector w toward a source in direction (Φ,θ) is given by
(1.15) |
An expression for the array correlation matrix is derived in terms of steering vectors. Substituting the signal vector x(t) from (1.13) in the definition of the array correlation matrix given by (8) leads to the following expression for the array correlation matrix:
|
(1.16) |
The first term on the right-hand side (RHS) of (1.16) simplifies to
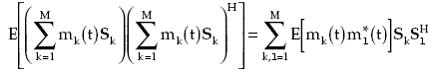 |
(1.17) |
When sources are uncorrelated,
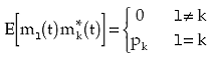 |
(1.18) |
where pk denotes the power of the kth source measured at one of the elements of the array. It should be noted that pk is the variance of the complex modulating function mk(t) when it is modeled as a zero-mean low-pass random process, as mentioned previously. Thus, for uncorrelated sources the first term becomes
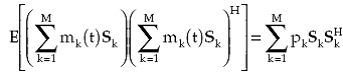 |
(1.19) |
The fact that the directional sources and the white noise are uncorrelated results in the third and fourth terms on the RHS of (1.16) to be identical to zero. This along with (1.19) lead to the following expression for the array correlation matrix when directional sources are uncorrelated:
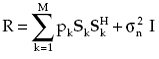 |
(1.20) |
(1.21) |
Let S0 denote the steering vector associated with the signal source of power PS. Then the array correlation matrix due to the signal source is given by
(1.22) |
Similarly, the array correlation matrix due to an interference of power PI is given by
(1.23) |
where SI denotes the steering vector associated with the interference.
Using matrix notation, the correlation matrix R may be expressed in the following compact form:
(1.24) |
where columns of the L * M matrix A are made up of steering vectors, that is,
(1.25) |
and M * M matrix S denote the source correlation. For uncorrelated sources, it is a diagonal matrix with
(1.26) |
In the next page conventional beamformer is introduced.
Back To Contents.