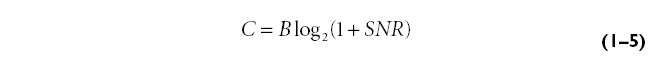|
The nature of the short-duration pulses used in UWB technology offers several advantages over narrowband communications systems. In this section, we discuss some of the key benefits that UWB brings to wireless communications.
ABILITY TO SHARE THE FREQUENCY SPECTRUM
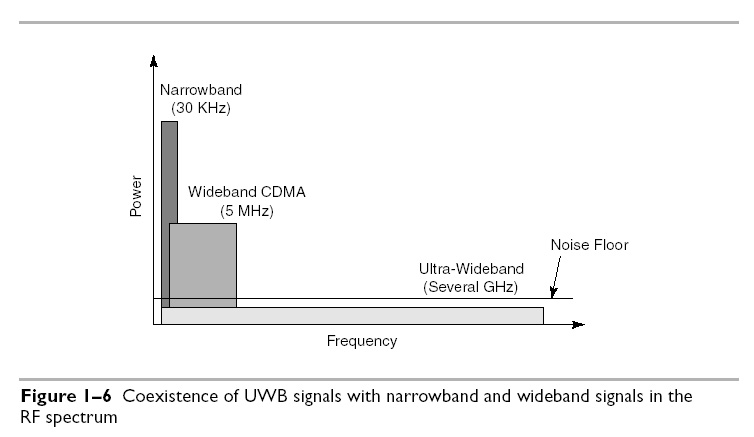
The FCC’s power requirement of –41.3 dBm/MHz,5 equal to 75 nanowatts/ MHz for UWB systems, puts them in the category of unintentional radiators, such as TVs and computer monitors. Such power restriction allows UWB systems to reside below the noise floor of a typical narrowband receiver and enables UWB signals to coexist with current radio services with minimal or no interference. However, this all depends on the type of modulation used for data transfer in a UWB system.
As we discuss in Chapter 3, some modulation schemes generate undesirable discrete spectral lines in their PSD, which can both increase the chance of interference to other systems and increase the vulnerability of the UWB system to interference from other radio services. In Chapter 4, we present a detailed discussion on interference from UWB on narrowband and wideband radio systems. Figure 1–6 illustrates the general idea of UWB’s coexistence with narrowband and wideband technologies.
LARGE CHANNEL CAPACITY
One of the major advantages of the large bandwidth for UWB pulses is improved channel capacity. Channel capacity, or data rate, is defined as the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted per second over a communications channel. The large channel capacity of UWB communications systems is evident from Hartley-Shannon’s capacity formula:
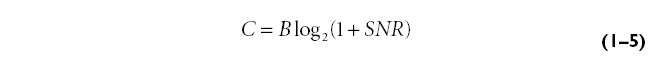
where C represents the maximum channel capacity, B is the bandwidth, and SNR is the signal-to-noise power ratio. As shown in Equation 1–5, channel capacity C linearly increases with bandwidth B. Therefore, having several gigahertz of bandwidth available for UWB signals, a data rate of gigabits per second (Gbps) can be expected. However, due to the FCC’s current power limitation on UWB transmissions, such a high data rate is available only for short ranges, up to 10 meters. This makes UWB systems perfect candidates for short-range, high-data-rate wireless applications such as wireless personal area networks (WPANs). The trade-off between the range and the data rate makes UWB technology ideal for a wide array of applications in military, civil, and commercial sectors. We explore such applications later in this chapter and in Chapter 5.
|