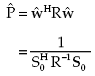
Output Signal-to-Noise
Ratio and Array Gain
The mean output power of the optimal processor is given by
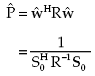 |
(4.30) |
This power consists of the signal power, residual interference power, and uncorrelated noise power. Expressions for these quantities are given by (4.17), (4.18), and (4.19), respectively. The total noise at the output is the sum of residual interference and uncorrelated noise. The expression for total noise power is given by (4.20).
Let α denote the SNR of the optimal beamformer, that is,
(4.31) |
It follows from (4.17) and (4.20) that
(4.32) |
It should be noted that the same result also follows from (4.8) and (4.13), the expressions for the signal power and the total noise power at the output of unconstrained beamformer. Thus, the constrained as well as unconstrained beamformer results in the same output SNR. The array gain of a beamformer is defined as the ratio of the output SNR to the input SNR. Let G denote the array gain of the optimal beamformer, that is,
| (4.33) | |
SNR at the input of the beamformer is then given by
|
(4.34) |
Thus,
|
(4.35) |
Optimal beamformer in the presence of uncorrelated noise only and one directional interference is discussed later.
Back to optimal beamformer .
Back To Contents .